Chocolate Milk as a Post-Workout Beverage
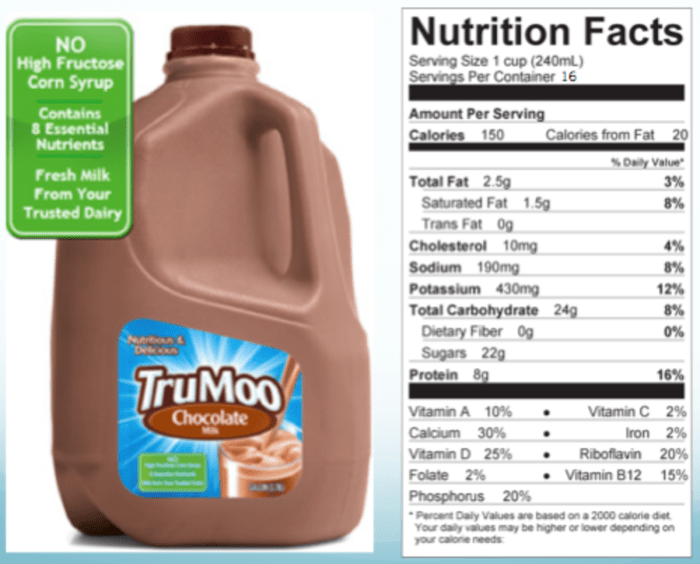
Chocolate milk nutrition facts – Chocolate milk has emerged as a surprisingly effective post-workout recovery drink, challenging the dominance of traditional sports drinks. Its naturally occurring blend of carbohydrates and protein makes it a convenient and potentially superior option for replenishing energy stores and aiding muscle repair after intense physical activity.The optimal post-workout recovery strategy involves replenishing glycogen stores (carbohydrates) and repairing muscle tissue (protein).
Understanding chocolate milk nutrition facts requires considering its components: milk and chocolate. The milk portion contributes calcium and protein, while the added chocolate impacts sugar and fat content. For a comparison of dairy fat content, you might find it useful to check out the nutritional information on half and half nutrition facts , as it offers a different perspective on dairy fat levels.
Returning to chocolate milk, remember that the specific nutritional values vary greatly depending on the brand and the amount of added sugar.
Carbohydrates provide the readily available energy needed to restore muscle glycogen levels depleted during exercise. Protein, on the other hand, is crucial for muscle protein synthesis, the process of repairing and building muscle tissue damaged during exercise. Insufficient replenishment of either can hinder recovery and impair future performance.
Carbohydrate and Protein Roles in Muscle Recovery
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. During exercise, muscle glycogen stores are depleted, leading to fatigue. Replenishing these stores quickly is essential for recovery and prevents future performance decrements. Protein, composed of amino acids, provides the building blocks for muscle repair and growth. After exercise, muscle protein breakdown increases, so adequate protein intake is necessary to counteract this catabolic process and promote anabolic (muscle-building) activity.
The ideal post-workout drink should therefore contain a balance of both carbohydrates and protein.
Chocolate Milk’s Suitability as a Post-Workout Recovery Drink
Chocolate milk offers a naturally occurring ratio of carbohydrates and protein beneficial for post-workout recovery. The carbohydrates in the milk sugar (lactose) provide readily available energy, while the milk protein (whey and casein) supports muscle repair. Furthermore, chocolate milk contains electrolytes, such as potassium and sodium, which are lost through sweat during exercise and contribute to hydration. The combination of these nutrients makes chocolate milk a convenient and potentially effective recovery beverage.
Studies have shown that chocolate milk can be as effective as, or even more effective than, some commercially available sports drinks in promoting muscle recovery and replenishing glycogen stores. For example, research has demonstrated comparable results in terms of muscle glycogen replenishment and perceived recovery between chocolate milk and commercially available carbohydrate-electrolyte beverages.
Comparison of Chocolate Milk to Other Sports Drinks
While many sports drinks contain carbohydrates and electrolytes, they often lack the protein content found in chocolate milk. This protein deficiency can limit their effectiveness in promoting muscle repair. Some sports drinks also contain high levels of added sugars, which can contribute to weight gain and other health concerns. In contrast, chocolate milk provides a more balanced nutrient profile, offering both carbohydrates and protein in a naturally occurring form, along with essential electrolytes, without excessive added sugars.
The relative cost-effectiveness of chocolate milk compared to specialized sports drinks is also a significant advantage. Therefore, while sports drinks can serve a purpose, particularly in prolonged or high-intensity endurance events, chocolate milk presents a compelling alternative for many individuals, particularly those engaged in moderate-intensity resistance or interval training.
Chocolate Milk and Different Age Groups
Chocolate milk, a popular beverage enjoyed by people of all ages, offers a unique blend of nutrients that can contribute to a balanced diet. However, its suitability varies depending on the individual’s nutritional needs and developmental stage. Understanding the specific requirements of different age groups is crucial in determining the appropriateness of chocolate milk as part of a healthy eating plan.
Nutritional Needs Across Age Groups and Chocolate Milk’s Role
The nutritional needs of children, adolescents, and adults differ significantly, impacting how chocolate milk fits into their overall dietary intake. Children require ample nutrients for growth and development, adolescents need energy to support rapid physical changes and increased activity levels, while adults focus on maintaining overall health and preventing age-related decline. Chocolate milk, with its combination of calcium, protein, and carbohydrates, can play a beneficial role in meeting some of these needs, but it should not be considered a sole source of nutrition.
Chocolate Milk Appropriateness by Age Group
| Age Group | Nutritional Benefits | Potential Concerns | Recommended Serving Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children (2-8 years) | Provides calcium for bone growth, protein for muscle development, and carbohydrates for energy. The added sugars can contribute to overall energy intake. | High sugar content can contribute to dental problems and weight gain if consumed excessively. Should be part of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. | 4-6 ounces, ideally low-sugar varieties or diluted with milk. |
| Adolescents (9-18 years) | Supports increased energy demands during growth spurts and physical activity. Calcium is crucial for bone density, and protein aids muscle development. | High sugar content may contribute to weight gain and acne. Should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet that includes nutrient-rich foods. | 8-12 ounces, preferably low-sugar or unsweetened versions. Consider timing consumption around physical activity. |
| Adults (19+ years) | Provides a convenient source of calcium and protein, especially beneficial for those with increased physical activity or those needing a post-workout recovery drink. | High sugar content can contribute to weight management challenges and chronic diseases. Those with pre-existing health conditions should consult a healthcare professional before regular consumption. | 8-12 ounces, occasionally, focusing on low-sugar or unsweetened varieties. |
Variations and Alternatives: Chocolate Milk Nutrition Facts
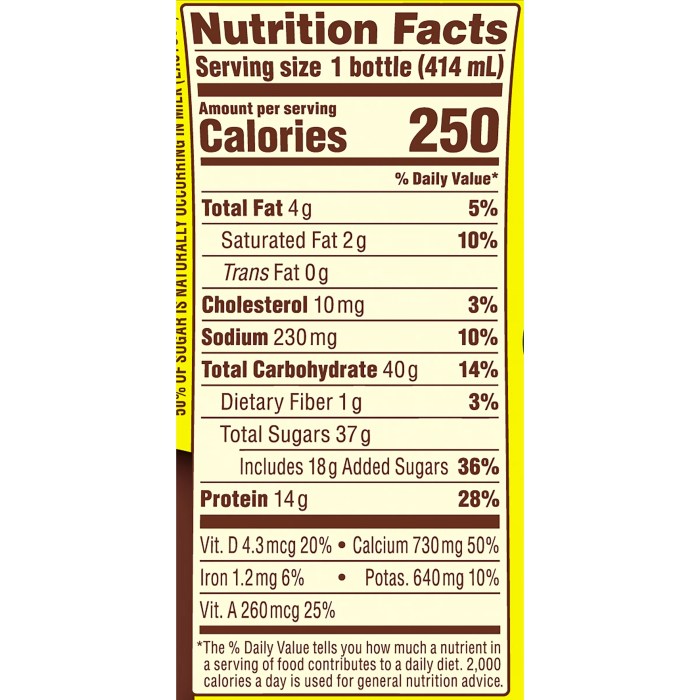
Chocolate milk isn’t just one thing; a range of options caters to different dietary needs and preferences. Understanding these variations and exploring healthier alternatives allows for informed choices about incorporating chocolate milk into a balanced diet. This section will explore the diverse world of chocolate milk and offer some nutritious substitutes.The most common variations center around the type of milk used and the presence of added sugars and other ingredients.
Traditional chocolate milk uses cow’s milk, but increasingly popular options include plant-based alternatives and organic varieties. These choices impact the nutritional profile significantly, influencing the fat content, protein source, and overall sugar levels.
Types of Chocolate Milk, Chocolate milk nutrition facts
Several types of chocolate milk are available, each with its unique nutritional composition. Traditional chocolate milk uses cow’s milk as a base, often fortified with vitamins and minerals. Organic chocolate milk utilizes milk from cows raised without the use of pesticides or hormones, offering a potentially cleaner product. Plant-based chocolate milk uses alternatives like almond, soy, oat, or coconut milk, making it suitable for those with lactose intolerance or following a vegan lifestyle.
These plant-based versions often have lower fat content than dairy-based options but may vary in protein and sugar levels depending on the brand and specific ingredients. For instance, soy milk tends to be higher in protein compared to almond milk. The addition of cocoa powder, chocolate syrup, or other flavorings further impacts the overall nutritional content.
Nutritional Differences Between Chocolate Milk Variations
Nutritional differences between chocolate milk variations are primarily driven by the type of milk used and the presence of added sugars. Dairy-based chocolate milk generally provides a good source of calcium and protein, but the fat content can be relatively high, particularly in whole milk varieties. Organic versions generally have similar nutritional profiles to their non-organic counterparts but may have a slightly different taste due to the farming practices.
Plant-based chocolate milk often has less saturated fat and cholesterol than dairy milk, but the protein content can be lower unless fortified. The sugar content can also vary widely between brands and types, with some containing significant amounts of added sugars. It’s crucial to check nutrition labels to compare different products and make informed choices based on individual dietary needs and preferences.
For example, comparing a serving of whole milk chocolate milk to a serving of unsweetened almond milk chocolate milk will reveal substantial differences in fat, sugar, and protein content.
Healthier Alternatives to Traditional Chocolate Milk
Many healthier alternatives to traditional chocolate milk offer similar satisfaction without the potential downsides of high sugar and fat content. Choosing these alternatives can contribute to a more balanced and nutritious diet.
- Homemade Chocolate Milk with Unsweetened Almond Milk and Cocoa Powder: This option allows for precise control over sugar and ingredient quality. Using unsweetened almond milk and cocoa powder minimizes added sugar and provides a good source of antioxidants from the cocoa.
- Smoothies with Fruits and Cocoa Powder: Blending fruits like berries or bananas with cocoa powder creates a naturally sweet and nutritious beverage. This adds fiber and vitamins from the fruits.
- Dark Chocolate and Milk (Dairy or Plant-Based): A small amount of high-quality dark chocolate (70% cacao or higher) melted into milk offers a rich chocolate flavor with potential health benefits from flavonoids, but watch portion size to control calories.
Clarifying Questions
Is chocolate milk suitable for lactose-intolerant individuals?
No, traditional chocolate milk contains lactose. Lactose-free or plant-based alternatives are available for those with lactose intolerance.
Can chocolate milk contribute to muscle growth?
Yes, the combination of protein and carbohydrates in chocolate milk can support muscle recovery and growth after exercise, making it a suitable post-workout beverage.
How does the nutritional content of chocolate milk compare to cow’s milk?
Chocolate milk generally has a higher calorie and sugar content than plain cow’s milk due to the added cocoa and sugar. However, it can provide similar amounts of protein and calcium.
Are there any potential risks associated with excessive chocolate milk consumption?
Excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain due to high sugar and calorie content. It can also negatively impact dental health.